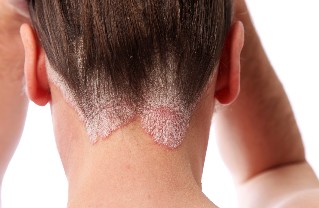
What is psoriasis
Psoriasis (psoriasis) is a non – contagious chronic skin disease that is manifested as flaking and rashes on the skin. Characterized by undulating course, with periods of remission (improvement), and through relapses. The disease can develop at any age, but most often psoriasis affects people of young age.
The intensity of psoriasis can vary greatly in different stages. The disease can affect only small areas of skin or cover the entire body. Often the disease progresses, patients report that over time (when the period of exacerbation) psoriasis affects a large area of skin. In addition, the skin also secretes the nail psoriasis, which can occur in isolated form.
Psoriasis – the causes of the disease
The cause of psoriasis is not known, but the disease can cause immunological changes in the body (auto-immune diseases, aggression), neurological disorders, metabolic disorders. Help psoriasis heredity, a weakened immune system after illness, stress.
To date, the reasons and factors, the development of psoriasis are:
- Genetic susceptibility (genetic theory to the development of psoriasis). The likelihood of developing psoriasis is greater, if the person has close relatives also suffer from this disease. Maybe some group of genes are responsible for psoriasis.
- Neuro-psychic overvoltage (neurogenic theory of the development of psoriasis). It is known that psoriasis can be triggered by extreme emotional upheaval. Stress causes serious factors for the development of this disease. In people with psoriasis, stress can cause an exacerbation of the disease.
- Hormonal disturbances. Changes in the endocrine glands can be the triggering mechanism for the development of psoriasis.
- A metabolic disorder (metabolic theory to the development of psoriasis). Problems with metabolism, some vitamins and minerals (particularly silicon) can contribute to the appearance of psoriatic plaques.
- Parasites. Discusses the parasitic theory of psoriasis development, according to which the disease is caused by certain intestinal parasites. Numerous studies show that among people who suffer from psoriasis, many carriers of different parasitic infections. Scientists believe that a special role in the development of the disease can play roundworm, Giardia, beef tapeworm, and others. It is believed that the toxic products that emit these parasites are powerful allergens, which cause an imbalance of the immune system.
- Virus infection.
And although the cause of psoriasis is not fully clarified so far, the drug has been known the mechanism of occurrence of this pathology. Based on the appearance of psoriatic rash violation of the immune system. Immune system cells become aggressive towards your own skin cells, which leads to the appearance of psoriatic plaques.
Psoriasis – symptoms
Psoriasis manifests itself in the appearance of scaly spots, red plaques that itch strongly. Spots usually located in the skin, scalp, elbow, knees, and areas where the skin folds. Over time, the surface scale can be easily removed, and in their place are a more dense scale, is placed in thoroughly. With the progression of psoriasis, there is the so-called phenomenon kebne in: the emergence of psoriatic plaques in places, scratches or skin injuries.
This is the symptoms that are typical for different psoriasis:
- Psoriasis in the form of plaques to show above the surface, healthy skin areas red, inflamed, dry, thickened, hot to the touch skin, covered with silvery white scales (psoriasis patches). The skin in these areas is prone to flaking. Condition the skin peel is still red lesions, which are easily injured and bleeding. Psoriatic plaques usually merge with each other, increasing in size and consists of a plate plaques ("paraffin lakes"). Psoriasis flexor surfaces peeling are mild. Although there are red spots, which are located in the skin folds (groin, the area of the external genitalia, inner thighs, tummy tuck, arm).
- Guttate psoriasis is characterized by a large amount of dry, small, red or purple lesions, raised above the skin surface, reminiscent of tears, or circles. These elements are striking in large areas of the skin. Guttate psoriasis often develops after suffering streptococcal infection (eg. pharyngitis or tonsillitis).
- Pustular psoriasis appears above the surface, intact skin bubbles filled with clear content. Pustules, surrounded by red, swollen skin, which easily peels off. Nail psoriasis is characterized by the color change of the nail, nail bed, the appearance of dots, spots, cross-streaks of the nails, thickening of the skin around the nail bed, thickening and stratification of the nail, complete loss of nails.
- Psoriatic arthritis is accompanied by inflammation processes in the joints and connective tissue. Psoriatic arthritis most commonly affects the small joints of distal phalanges of hands, feet, what causes psoriatic dactylitis. Psoriatic erythroderma seems to be a widespread exfoliation and inflammation, peeling, skin a large surface of the body, swelling, tenderness of the skin, intense itching.
Other symptoms of psoriasis are:
- bleeding area on the skin;
- the appearance of erosions and pits on the nails;
- severe itching;
- possible joint pain and swelling.
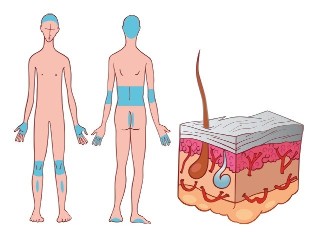
Classification of psoriasis
The following types of psoriasis:
- vulgar (or common) of psoriasis;
- exudative psoriasis;
- arthropathic psoriasis;
- psoriatic erythroderma;
- psoriasis, palms and soles;
- pustular psoriasis.
Psoriasis takes place in three stages:
- The progressive stage of psoriasis. This is the first stage of the disease, which is characterized by fever, which is increasing the amount of fresh damage.
- The stationary phase of psoriasis. This period is characterized by the preservation of the existing pattern of disease. Rash and other symptoms of psoriasis is not getting no more, no less.
- Stage of psoriasis which retreats. This is the last phase of the disease, where the lesions are gone.
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process in psoriasis happens:
- limited affects smaller areas of the body;
- common – affects large areas of the body;
- generalized – affects almost all body.
Depending on the season, when the disease is acute, psoriasis happens:
- winter – exacerbation of psoriasis usually occurs in the cold season;
- summer – exacerbation of psoriasis occurs in the summer;
- uncertain – when the periods of exacerbation of psoriasis are not related to any season of the year.
The diagnosis of psoriasis
To diagnose the disease with a dermatologist on the basis of typical clinical picture. To clarify the diagnosis used skin biopsy.
Patient
You can take a sun bath for 15 minutes daily. You should refrain from drinking alcohol, avoid stress, watch your weight, maintain a healthy lifestyle to properly care for the skin.
Treatment of psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment to use emollients and medications that restore the stratum corneum, topical preparations (ointments, creams, lotions) with the content of corticosteroids (hydrocortisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone), preparations containing pyrithione zinc cream, which contains vitamin D3 analogues, tar, naphthalene, hydroxyestra your. In psoriasis, the ineffectiveness of topical treatment, lesions of more than 20% of the skin surface of the prescribed systemic drug therapy, which includes cytotoxic (methotrexate), synthetic retinoids (vitamin a acetate, retinol palmitate, tretinoin), glucocorticoids, multi-vitamins (aevit, etc.).
A special role in the treatment of psoriasis should be due to some biologically active substances, among which should be noted:
- Silicon. In recent years doctors are increasingly talking about the role of silicon in the development of psoriasis. One part of the treatment of psoriasis are medications and vitamin-mineral complexes, which contain silicon. On the other hand, silicon improves the condition of skin, and the second – works of the sorbent, which absorbs the antigens that play a role in the development of psoriasis.
- D-vitamin. As you know, one of the most important minerals necessary for a successful fight against psoriasis is calcium. However, the proper absorption of calcium is needed vitamin D best vitamin D products set after the transfer of the active phase of psoriasis inpatient treatment.
- Fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids. To remove the inflammatory process in psoriasis is necessary that the intake of polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acids, which in large quantities contained in fish oil.
- Lecithin. This substance is needed for rapid restoration of epithelial cells that die psoriasis. Preparations lecithin can be used to quickly deal with the inflammation and restore the integrity of the skin.
Non-drug treatment is systemic photochemotherapy uv-a radiation, whose wavelength is 320-400 NM on the background of the reception of light (PUVA-therapy). Also, cold treatment, plasmapheresis.
The patient must follow a special diet. Diet for psoriasis should be balanced. The patient should be excluded from the diet of processed food, spicy food and sweets. You need to carefully monitor their health and avoid colds, such as violation of immunity might trigger the development of the disease.
Complications
Among the possible complications arthritis, depression caused by low self-esteem.

Prevention of psoriasis
Disease prevention is impossible, but there are ways to relieve psoriasis symptoms and reduce exacerbations. It is necessary to protect the skin from drying, avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, try to prevent damage to the skin. Avoid stressful situations, infections, medications that increase the symptoms of psoriasis (eg., β-blockers, lithium), quit Smoking, limit alcohol consumption. And remember that treatment of psoriasis should be entrusted to professionals. Psoriasis treatment at home and all kinds of self-medication in this disease is unacceptable.
























